Hearing Loss
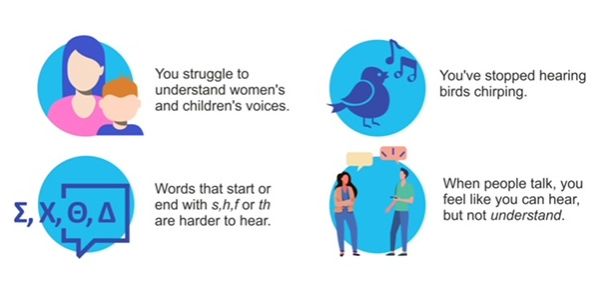
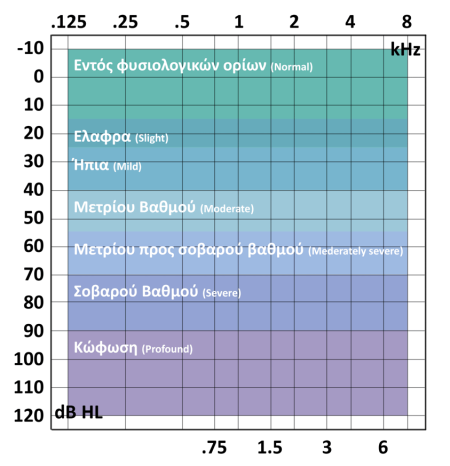
Hearing loss is a reduction in hearing as depicted on the audiogram. It is considered a drop below 20 or 25 dBHL.
CAUTION: Hearing loss is not the same as deafness
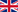
Depending on the degree of hearing loss, various challenges arise. At times, consonants and phonemes are not accurately discerned. In several instances, syllables may be unclear, leading to confusion between the /b/ and /g/ phonemes. Frequently, individuals with hearing loss find themselves in a situation where they must guess the word to comprehend the conversation.
Degrees of Hearing Loss and perceprion
This pictures shows the HL. The degrees may vary.
| Hearing Loss | Audiogram | Perception of HL | |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
Normal hearing |
All sounds are audible <20 dBHL |
Speech is understood even In noisy environment |
 |
Mild |
Hearing loss is between 20- 40dBHL |
Difficulty understanding speech in noisy environment |
 |
Moderate |
Hearing loss is between 41-70dBHL |
Difficulty understanding speech during conversation |
 |
Severe |
Hearing loss is between 71- 95dBHL |
Extremely difficult to understand speech without hearing aid |
 |
Profound |
Hearing loss is above 95 dBHL |
Hearing aid or cochlear implant is necessary |
Hearing loss degrees
Mild hearing loss
The child has difficulty hearing low intensity speech especially in noisy environments
Moderate hearing loss
Difficulty of hearing even when close
Severe hearing loss
The child can only hear very loud sounds such as sirens, slumping doors etc
Profound Hearing Loss
The child perceives very loud sounds as vibration.
dBHL
Hearing Loss Types
Are there different types of hearing loss?
Yes. There are 3 basic types of hearing loss. Conductive hearing loss, sensorineural hearing loss and much more rarely mixed hearing loss
What are types of hearing loss?
It usually occurs when there is a dysfunction or a pathological condition related to the outer and inner ear
Some causes are:
- ear wax (impacted)
- eardrum perforation
- exostosis
- otosclerosis,
- otitis media
- cholesteatoma, etc.
In these cases, the sound cannot be transmitted normally to the cochlea, which is the main organ of hearing.
In sensorineural hearing loss there is a disorder in the cochlea or auditory pathway that carries sound to the brain.
Sensorineural hearing loss is defined by:
- the frequency range in which it occurs (e.g. low or high frequency)
- the shape of the audiogram (flat or down sloping) and
- the degree of hearing loss (small, medium or large)
Mixed hearing loss is a combination of sensorineural hearing loss and conductive hearing. The causes of mixed hearing loss are different from the causes listed above
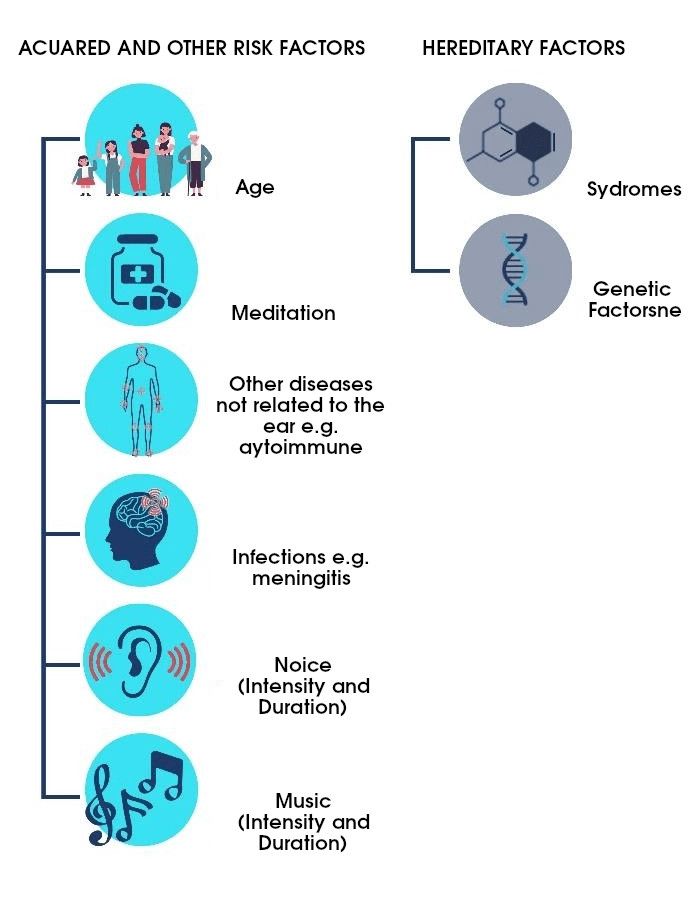
There are both hereditary and acquired factors associated with hearing loss.
-
Symptoms associated with congenital hearing loss can occur
- either in infancy
- or at ages after the second or third decade of life.
Approximately 70% of all mutations that cause hearing loss are non-syndromic. This means that the person has no other symptoms.
About 30% of mutations that cause hearing loss are syndromic. This means that the person has symptoms other than hearing loss.
(Read more: here and here) -
Acquired factors and other factors include:
- ototoxic drugs
- presbyacusis: this is a condition related to the effect of age on the hearing system. A similar condition occurs in the eyes and is called presbyopia.
- noise: Occupational exposure to noise is the second most common risk factor in the workplace, after injuries (WHO Europe, 2017). Noise exposure contributes to 22% of workplace-related health problems. Many studies show that exposure to occupational noise directly leads to hearing loss (Safe Work Australia, 2010; Mahboubi et al., 2013).